
Thus, Angle of incidence, i =Angle of reflection, r
The 2nd law of reflection states that: The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal to the reflecting surface are coplanar.
By coplanar it is meant that they lie on the same plane.
- 36
- The Role of Light to Sight
- The Line of Sight
- The Law of Reflection
- Specular vs. Diffuse Reflection
Light is known to behave in a very predictable manner. If a ray of light could be observed approaching and reflecting off of a flat mirror, then the behavior of the light as it reflects would follow a predictable law known as the law of reflection. The diagram below illustrates the law of reflection.
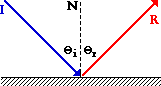
In the diagram, the ray of light approaching the mirror is known as the incident ray (labeled I in the diagram). The ray of light that leaves the mirror is known as the reflected ray (labeled R in the diagram). At the point of incidence where the ray strikes the mirror, a line can be drawn perpendicular to the surface of the mirror. This line is known as a normal line (labeled N in the diagram). The normal line divides the angle between the incident ray and the reflected ray into two equal angles. The angle between the incident ray and the normal is known as the angle of incidence. The angle between the reflected ray and the normal is known as the angle of reflection. (These two angles are labeled with the Greek letter "theta" accompanied by a subscript; read as "theta-i" for angle of incidence and "theta-r" for angle of reflection.) The law of reflection states that when a ray of light reflects off a surface, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.

It is common to observe this law at work in a Physics lab such as the one described in the previous part of Lesson 1. To view an image of a pencil in a mirror, you must sight along a line at the image location. As you sight at the image, light travels to your eye along the path shown in the diagram below. The diagram shows that the light reflects off the mirror in such a manner that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
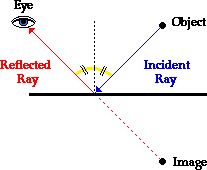
It just so happens that the light that travels along the line of sight to your eye follows the law of reflection. (The reason for this will be discussed later in Lesson 2). If you were to sight along a line at a different location than the image location, it would be impossible for a ray of light to come from the object, reflect off the mirror according to the law of reflection, and subsequently travel to your eye. Only when you sight at the image, does light from the object reflect off the mirror in accordance with the law of reflection and travel to your eye. This truth is depicted in the diagram below.
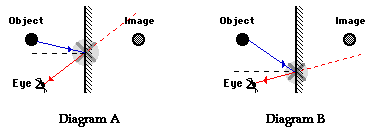
For example, in Diagram A above, the eye is sighting along a line at a position above the actual image location. For light from the object to reflect off the mirror and travel to the eye, the light would have to reflect in such a way that the angle of incidence is less than the angle of reflection. In Diagram B above, the eye is sighting along a line at a position below the actual image location. In this case, for light from the object to reflect off the mirror and travel to the eye, the light would have to reflect in such a way that the angle of incidence is more than the angle of reflection. Neither of these cases would follow the law of reflection. In fact, in each case, the image is not seen when sighting along the indicated line of sight. It is because of the law of reflection that an eye must sight at the image location in order to see the image of an object in a mirror.
- 0
The Law of Reflection
- The Role of Light to Sight
- The Line of Sight
- The Law of Reflection
- Specular vs. Diffuse Reflection
Light is known to behave in a very predictable manner. If a ray of light could be observed approaching and reflecting off of a flat mirror, then the behavior of the light as it reflects would follow a predictablelawknown as thelaw of reflection. The diagram below illustrates the law of reflection.
In the diagram, the ray of light approaching the mirror is known as theincident ray(labeledIin the diagram). The ray of light that leaves the mirror is known as thereflected ray(labeledRin the diagram). At the point of incidence where the ray strikes the mirror, a line can be drawn perpendicular to the surface of the mirror. This line is known as anormal line(labeledNin the diagram). The normal line divides the angle between the incident ray and the reflected ray into two equal angles. The angle between the incident ray and the normal is known as theangle of incidence. The angle between the reflected ray and the normal is known as theangle of reflection. (These two angles are labeled with the Greek letter "theta" accompanied by a subscript; read as "theta-i" for angle of incidence and "theta-r" for angle of reflection.) The law of reflection states that when a ray of light reflects off a surface, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
It is common to observe this law at work in a Physics lab such as the one described in the previous part of Lesson 1. To view an image of a pencil in a mirror, you must sight along a line at the image location. As you sight at the image, light travels to your eye along the path shown in the diagram below. The diagram shows that the light reflects off the mirror in such a manner that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
It just so happens that the light that travels along the line of sight to your eye follows the law of reflection. (The reason for this will be discussed later in Lesson 2). If you were to sight along a line at a different location than the image location, it would be impossible for a ray of light to come from the object, reflect off the mirror according to the law of reflection, and subsequently travel to your eye. Only when you sight at the image, does light from the object reflect off the mirror in accordance with the law of reflection and travel to your eye. This truth is depicted in the diagram below.
For example, in Diagram A above, the eye is sighting along a line at a positionabovethe actual image location. For light from the object to reflect off the mirror and travel to the eye, the light would have to reflect in such a way that the angle of incidence is less than the angle of reflection. In Diagram B above, the eye is sighting along a line at a positionbelowthe actual image location. In this case, for light from the object to reflect off the mirror and travel to the eye, the light would have to reflect in such a way that the angle of incidence is more than the angle of reflection. Neither of these cases would follow the law of reflection. In fact, in each case, the image is not seen when sighting along the indicated line of sight. It is because of the law of reflection that an eye must sight at the image location in order to see the image of an object in a mirror.
- 0

